Daniel
| 1. |
Why a commentary on Daniel. |
| A grasp of Daniel is necessary for understanding the Book of Revelation. The two are tied together in the way they present prophecy.
| |
| 2. | What does his name mean?
|
| Daniel means God is my judge. | |
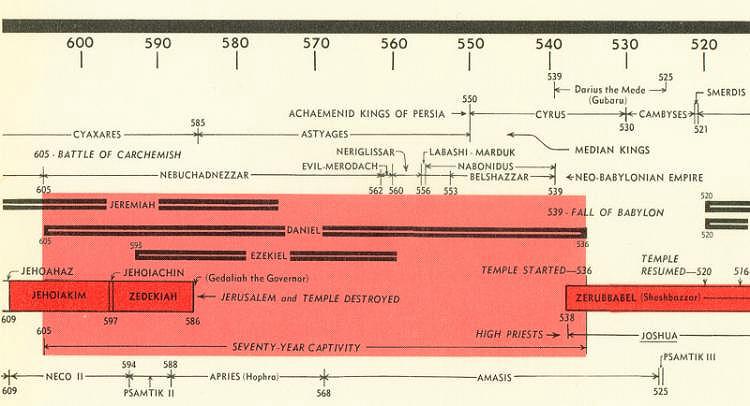
| 3. | The times when Daniel had his experiences. |
| King David ruled in 1,000 B. C. He was followed by his son Solomon who ruled Israel about 40 years. Under Solomon's son Rehoboam, the nation
divided into Israel in the north and Judah in the south. After several hundred years of idolatry, Israel was carried off to Assyrian captivity. | |
| a. | 605 B. C. - Battle of Carchemish, establishing Babylonian domination. |
| (1) Pharaoh-Necho of Egypt came to fight the Babylonians at
Carchemish (2) Nebuchadnezzar defeated the Egyptians, chasing them south through Judah (3) At Jerusalem, Nebuchadnezzar heard of his father's death; he returned to assume the throne in Babylon (4) The first group of Jewish captives were taken, along with Daniel and his friends -Dan 1: 1-4 | |
| b. | 597 B. C. -A second remnant taken to Babylon. |
| (1) Jehoiachin (Jeconiah, Coniah) followed the reign of his father, Jehoiakim. (2) Eleven years later, Jerusalem was totally devastated by Babylonian forces -2 Kin 25: 1-10. (3) This second group of captives included Ezekiel -Eze 1: 1-3. | |
| c. | 586 B. C. - Fall of Jerusalem and the temple destroyed. |
| (1) Zedekiah was installed as king in Jerusalem, but was weak and vacillating. (2) Eleven years later, Jerusalem was totally devastated by Babylonian forces -2 Kin 25: 1-10. (3) A third group was taken into Babylonian captivity, but Jeremiah was among those who stayed behind -2 Kin 25: 11-12,22; Jer 39: 11-14; 40: 1-6. | |
| d. | 536 B. C. - The first remnant returns to Jerusalem. |
| (1) Babylon falls in 539 B. C. (2) Cyrus, king of Persia, sends the first remnant back under the leadership of Zerubbabel -Ezra 1: 1-5; 2: 1-2. (3) The foundation of the temple was soon started, but the temple was not completed until 516 B. C. -Ezra 3: 8-13; 6: 14-16. | |
| 4. | When did Daniel live? |
| a. | Daniel was contemporary with Jeremiah and Ezekiel. See the time line chart. |
| (1) Jeremiah prophesied in Jerusalem before and during the
Babylonian exile. (2) Ezekiel prophesied in Babylon among the exiles. (3) Daniel prophesied in the capital of Babylon. | |
| b. | Daniel lived about 600 B. C. See the time line below. |
| (1) He descended from one of Judah's prominent families, if not from royal blood. Daniel 1: 3 (2) At an early age, he was taken from his family to be trained in the courts of Babylon. Daniel 1: 3-4 (3) Whether he ever married is uncertain. |

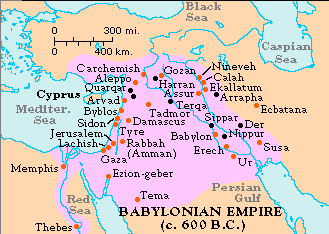
| 5. |
Where was Babylon and the Babylonian Empire? |
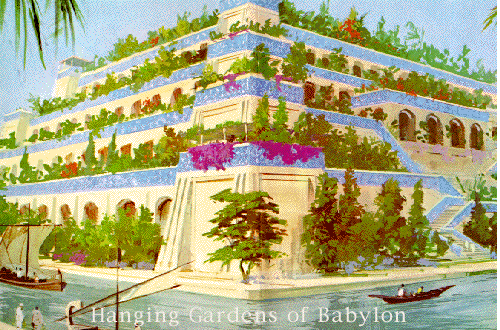
| 6. |
What were the Hanging Garden of Babylon? |
| Below is an artist's conception. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon rise on terraces some 400 feet above the level of the plain. This hanging garden were built by Nebuchadnezzar about 600 B. C. to console his queen, who missed the mountains, trees and flowers of her native Media. |
| 7. |
The case for Daniel's Inspiration. |
| a. | Daniel claims inspiration. 9: 21 -22. |
| b. | Jesus endorsed his writing, calling him a prophet. Matthew 24: 15 |
| c. | Jesus quoted Daniel in Matthew 26: 64 |
| d. | Ezekiel, himself a prophet, quotes God as commending Daniel. Ezekiel 14: 14, 20; 28: 3. |
| 8. | Did Daniel write the book? |
| a. | Religious liberals do not want to accept the clear teaching of the book, and so assign later dates than the book claims for itself. They are very intelligent and can call the writer of the book a liar even though they are 2500 years removed from the time of writing. Prior to the discovery of the Dead Sea Scrolls, liberals claimed it was written after the time of Jesus by Christians. It's discovery among the scrolls (dated by radiocarbon dating to a period before Jesus) quieted this claim. |
| b. | Edward J. Young in The Prophecy of Daniel, published by Eerdmans, gives five lines of evidence proving the Daniel of whom the book testifies is the author of the book: |
| (1) In the second half of the book Daniel names himself (speaking in first person) as the one receiving the revelations, and he is ordered to preserve the book in which these words are found (12 :4). (2) It should be obvious to any honest reader that the book is the work of one person throughout. The first part prepares for the second; all sections are mutually related to one another; the historical narratives are interdependent; the character of Daniel is always the same. (3) Jesus Christ validates its authorship by Daniel (Mt. 24: 15). One should also compare Mt. 10: 23; 16: 27 ff; 19 :28; 24 :30; 25 :31; 26: 64. (4) The Septuagint and the books of Maccabees show definite influence by the book of Daniel. Jewish tradition attributes its authorship to this Daniel. (5) The book is saturated with historical nuances of Babylonian and Persian background. It had to be written by a person contemporary with the events. | |
| 9. | When was Daniel written? |
| H. C. Leupold dates the writing of this book between 538-528 B. C. Merrill C. Tenney gives "shortly after his last vision, in 536 B. C." as the date. Keil and Delitzsch say it was written "during the exile" by Daniel. Edward J Young agrees with the above statements. Practically all conservative scholars date the book somewhere near 536 B. C. – Paul T. Butler | |
| 10. | Why was Daniel written in two languages? |
| As to the question of why half the book was written in Aramaic (first half) and half in Hebrew (last half), the reason for the choice is fairly obvious. | |
| Those portions of Daniel's prophecy which deal generally with Gentile affairs were put into a linguistic medium which all the public could appreciate whether Jew or Gentile, But those portions which were of particularly Jewish interest were put into Hebrew in order that they might be understood by the Jews alone. – Paul T. Butler | |
| 11. | What roles did Daniel fill? |
| a. | An example for other advisors-in-training. Chapter 1 |
| b. | Dream-Interpreter as in chapter 2. |
| c. | Interpreter of Signs as in chapter 5. |
| d. | d. Seer of Visions as in chapter 7. |
| e. | e. Official of Kings. In addition to his duties as seer and as interpreter of signs and dreams, Daniel also stood high in the governmental service of Nebuchadnezzar, Belshazzar, and Darius the Mede, and perhaps also of Cyrus. The Book of Daniel, our only reliable source of information on this subject, does not tell us much about his civil duties and performances. It does say, however, that he was chief of the wise men, that he was in the gate of the king, and that he was governor over the whole province of Babylon under Nebuchadnezzar; that Belshazzar made him the third ruler in his kingdom; and that Darius made him one of the three presidents to whom his hundred and twenty satraps were to give account; and that he even thought to set him over his whole kingdom. In all of these positions he seems to have conducted himself with faithfulness and judgment. – International Standard Bible Encyclopedia |
| 12. | What Bible Translation is used in these Daniel notes? |
| We have used the American Standard Version of 1901 because of its accuracy and to avoid copyright concerns. Other translations are cited in the comments portion when they add clarity. |
Note: We have frequently referred to Paul T. Butler's DANIEL, published by College Press in 1970. The book is not in print, but is available as a download from: http://www.abarc.org/Bible%20Study%20Textbook%20Series/Books/Daniel/Daniel.htm This address is valid in January of 2004.
The Next Chapter
Chapter Key Words
Outline of Daniel
by Ralph Johnson1:
Captives
I. THIRD YEAR OF JEHOIAKIM, KING OF JUDAH
Commission of Daniel, Shadrach, Meshach and Abednego
2:
Image
II. SECOND YEAR OF NEBUCHADNEZZAR OF BABYLON
Nebuchadnezzar's dream:
Image with head of gold,
Arms and shoulders of silver,
Belly and thighs of brass,
Legs of iron,
Feet of clay and iron mixed.
Daniel's interpretation --
Little stone destroys them and fills the earth.
3:
Furnace
Conspiracy to destroy Daniel's companions.
Three young men in furnace for not worshiping an image. Enemies thrown into the furnace.
4:
Tree
Nebuchadnezzar's dream of the tree chopped down.
Daniel's interpretation
Fulfillment
Nebuchadnezzar's madness and restoration
5:
Writing
Belshazzar's feast.
Handwriting on the wall.
Fall of Babylon to the Medes
6:
Lions
Darius, the Mede, king of Persia throws Daniel into lions' den for praying.
7:
Beasts
III. FIRST YEAR OF BELSHAZZAR OF BABYLON
Daniel's dream: Four beasts,
Like a lion, with eagle's wings,
Like a bear, with three ribs in its mouth,
Like an Leopard, with four wings like a bird and four heads,
Ten horns with, great iron teeth, little horn.
8:
Goat
IV. THIRD YEAR OF THE REIGN OF BELSHAZZAR
Ram and he-goat battle (Persia and Greece)
Little horn (Antiochus Epiphanies)
9:
Seventy
V. FIRST YEAR OF DARIUS THE MEDE
Daniel's prayer for his people. (9: 1-19)
Seventy weeks to the Messiah. (9: 20-27)
(From Decree of Artaxerxes, 457 BC)
10:
Angels
VI. THIRD YEAR OF CYRUS OF PERSIA
Vision of the great man. (10: 1-9)
Daniel comforted (10: 10-17)
Daniel strengthened (10: 18-21)
11:
Greece
Greece and Egypt from Cyrus to Antiochus Epiphanies
12:
How Long?
Time of trouble to the resurrection. (12: 1-4)
"Time, times and a half" (12: 7)
1290 days. (12: 11)
1335 days. (12: 12)